One of the most important facets of public health is understanding epidemiological studies. I might also add that it is the one thing I repeatedly have to look over and a lot of my peers and colleagues find confusing and struggle with.
A quick recap of what epidemiology is – Put simply, it deals with figuring out the who, what, when, where, why and how certain diseases happen and telling us the way we can overcome/stop it.
Now epidemiology is actually made up of both Observational and Interventional studies, and to start we will talk about observational studies.
They are quite self-explanatory, as they are just that – observational. All we are doing is essentially just having an overall look. However, there are different ways to do this, and that is by being either descriptive or analytical.
So what are the main differences between these two types of research/studies we can carry out and what do we gain from it? I prefer the 5W’s and 1 H method of thinking about it.
| Descriptive | Analytical |
| Who? What? When? Where? | Why? How? |
So descriptive studies, look at an overall picture. It tells us what is going on, what is involved, who is involved, where it is happening and when without telling us Why or How. We basically go in without an idea for cause and effect. It essentially helps us identify them by examining patterns and by giving us an overall idea of the population, the distribution of health based on age, gender, location and time/over a period of time. It is from this, that we might identify a problem leading to ideas for new studies to figure out the why, how and perhaps even move on to an interventional study.
If let’s say I was selling chocolate and I wanted to know more about my customers, my initial descriptive study would tell me about the people who are buying my chocolates, where they live etc. I might learn, that only hipsters in their late 20’s buy my brand of chocolate but I still do not know why (well maybe because it’s unheard of?). My next task is to figure out why and perhaps how I can make my chocolate more appealing to different groups.
Examples of descriptive studies can be further broken down to cross-sectional study=ies like a health survey, ecological studies or even case reports/case series. Remember all it does, is present the facts for what they are and is a starting point for us to make associations and come up with new ideas.
Analytical studies then basically go into how this is happening and why? It is one of the ways to investigate causal relationships. So in these studies, I have a hypothesis/an idea. A health-related example would be that ‘smokers have a higher risk of lung cancer than non-smokers. We then investigate if this is true or not. How we go about this, is either with a case-control study, cohort study, cross-sectional study or an ecological study.
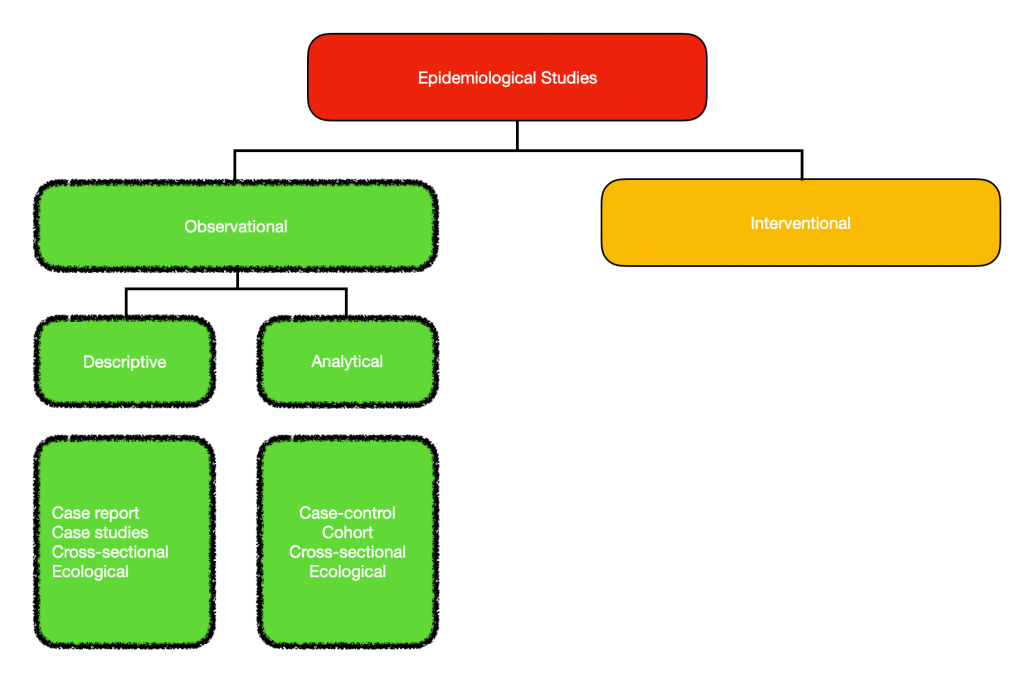
How come cross-sectional and ecological studies are in both descriptive and analytical studies? Well, I will go into that when I talk more about the different types of studies mentioned in the next post.